James Webb Space Telescope launch live blog: the entire launch as it happened
Relive the successful Christmas day launch of the next-gen telescope

Today is launch day for the James Webb Space Telescope aboard Arianespace’s Ariane 5 rocket, and we're covering all the latest updates as the mission counts down to its anticipated 7:20AM EST lift off.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the next generation observation platform and the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope. Built to detect deep into the infrared spectrum, the James Webb Space Telescope will be able to see deep into the history of the universe.
The oldest galaxies and stars from the very beginning of the universe can only be seen in this deep infrared space, so there's no telling what we'll see once Webb is online and operational.
After its successful launch, it will take 29 days for Webb to fully deploy at the second Lagrange point relative to Earth and the Sun, known as L2, a location about 1 million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from us.
Here, the larger universe will be far more visible to Webb than if it was located in low Earth Orbit like the Hubble Space Telescope, but it is also a far more complex deployment than Hubble was.
Essentially, if something physically goes wrong during the deployment, there's no way to recover and the $10 billion dollar instrument will be effectively useless. The 29 days until Webb completes its maneuvers and deploys at L2 will be some of the most intense and stressful time in recent memory for NASA, possibly since we first sent astronauts to the Moon in 1969.
And it all begins in just a few hours, and we'll be here to keep you updated on the entire launch and deployment as it happens.
Welcome to TechRadar's James Webb Space Telescope launch live blog! This is John, TechRadar's resident science geek, and I obviously can't tell you how excited we all are for this launch.
It truly is a historic moment for NASA, as this is absolutely one of the most complex space missions it has ever undertaken. There are nearly 350 single points of failure where the entire mission can collapse and we essentially have a $10 billion derelict flying off into space after nearly two decades of work.
Needless to say, these next 29 days are going to be the proverbial month from hell, and I know I for one will be following Webb's progress for the next four weeks and keeping you all updated as we go.
Merry Christmas to one and all, by the way!

The Ariane 5 rocket is fueling up as we speak and everything is on track for a launch in about an hour.
So let's talk about some James Webb Space Telescope facts.
The James Webb Space Telescope is a $10 billion project that began almost as soon as the Hubble Space Telescope became fully operational following a critical repair in 1993.
As a so-called "warm telescope", Hubble would never be able to fully see the infrared spectrum of light due to interference from the Earth, the Sun, and even its own optical instruments.
Additionally, there is the difficulty that comes from space dust surrounding Earth.
In order to get the best view of the universe possible, Webb needs to be incredibly cold (about -388 degrees Fahrenheit/ -233 degrees Celsius) and incredibly far away from the Earth at a distance of about 1 million miles (1.5 million kilometers).

So what's so important about infrared?
In the above picture, we have two different views of the famous Pillars of Creation in the Eagle nebula. The image on the left was taken by Hubble using visible light. See all that dust?
The image on the right is the same Pillars of Creation taken by Hubble's limited infrared sensors. As you can see, light that was obscured by the dust of the nebula has no problem passing through, and we can see all kinds of stars behind it that we couldn't see before.
That's one reason for the importance of infrared. The second, and arguably most important, is that the oldest galaxies and stars in the universe, those that formed more than 13.5 billion years ago, have been so red-shifted that their light is deep into the infrared spectrum.
We can't see this light now, but with Webb we will be able to, and we have no idea what the universe will look like at this wavelength of light. It's very exciting stuff.
We are less than 30 minutes from launch!
Also, why French Guiana? Besides being a joint effort between NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency (and so we might have wanted to throw the ESA a bone by launching Webb from one of its facilities), French Guiana is also on Earth's equator.
The speed of the Earth's rotation at the equator is actually faster than it is anywhere else, so launching in the same direction as the rotation of the Earth actually gives the Ariane 5 rocket that will be carrying Webb into space a bit of a boost, helping it get up the speed necessary to slingshot the telescope out to its destination 1 million miles away.
If you've got a few minutes before lift-off to take a look at what Webb's deployment schedule and process will look like, check out the above video produced by Northrup Grumman, the main contractor for the Webb telescope.
There are 344 single points of failure during the entire deployment that can scuttle the entire mission and render Webb useless, so each one has to come off successfully, and many of which represent the first time we've ever attempted something like it, so we also have to get a lot of things right on the first attempt.
Without question, this is the most complex space mission we've attempted since probably the Apollo Moon landings.

We are 10 minutes away from lift-off!
T-minus 2 minutes!
One minute!

We have lift-off!
We have LIFTOFF of the @NASAWebb Space Telescope! At 7:20am ET (12:20 UTC), the beginning of a new, exciting decade of science climbed to the sky. Webb’s mission to #UnfoldTheUniverse will change our understanding of space as we know it. pic.twitter.com/Al8Wi5c0K6December 25, 2021
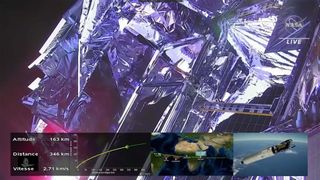
The fairings have been jettisoned and Webb is exposed to space with all systems nominal.
Main stage shutdown and separation successful.
Second stage ignition is nominal, rocketing Webb to its initial orbit around Earth at 7km/s.
In order to protect Webb's instruments from overheating, the second stage rocket will be performing a "sawtooth" maneuver, where it will adjust its side to side trajectory 30 degrees in both directions.
We are waiting to hear that there is electrical current flowing through the telescope's solar array.
We're about six minutes away from second stage cut off.
Wow, that mission control room looks quiet right now. It's easy to forget that this is the culmination of months of work for these people. They must be more anxious than anyone else.

Jean Luc Boyer (?) is the lead mission controller, apparently. He's the only one talking right now and he keeps saying nominal, so we're in good shape.
Second stage cut-off is successful!
Mission controllers in Baltimore are reporting that all systems in Webb look good. The telescope is coasting right now and is set to separate from the upper stage engine in about 20 seconds.
Second stage separation is successful! The James Webb Space Telescope is now flying under its own power!

The James Webb Space Telescope has been successfully been inserted into orbit and we have confirmation that its solar array is providing power to the telescope.
The first stage of Webb's deployment has been successful, and now it begins its "29 day on the edge", as NASA calls it.
Assuming everything goes as planned, it will take several months for the James Webb Space Telescope to cool down sufficiently for it to start snapping images of the universe in deep infrared.
This, of course, will be Webb's real test. It wasn't until Hubble first started taking images that we realized that its mirror hadn't been ground properly and that there were spherical aberrations on the images.
If something like that happens with Webb, there won't be much we can do but maybe try again. That will be a heartbreaking moment after so much work and anticipation, but science is a story of heartbreak as well as triumph.
How it will all turn out remains to be seen, but its off to a good start.

Understandably, there is a lot of celebration going on right now.
It might be a some months before we learn whether Webb is truly successful, but there's no doubt that the first stage of its mission was a success and a genuine feat of human engineering in its own right.
Launching stuff into space is hard work, and sometimes we forget that because engineers make it look so damn easy, but it's really not.
The James Webb Space Telescope is an incredibly delicate scientific instrument, with it's five sunshield panels being about the thickness of a human hair and covering an area the size of a tennis court, its folded 21.5-foot-tall primary mirror, and any number of instruments on board that can get knocked loose by literally riding a rumbling stream of fire against the force of gravity into outer space.
The fact that everything went off without a hitch is a testament to human ingenuity, and it never fails to impress the hell out of me every time I watch a successful rocket launch.

I'll second the sentiment of Jean-Luc Voyer after the successful second stage separation: Bon Voyage, James Webb. And for what it's worth to everyone involved in today's launch, Congratulations. It's a hell of a thing to have accomplished.
I don't want to leave things off without talking about some of the controversy around the James Webb Space Telescope. Many activists, scientists, and NASA personnel are upset about the naming of the telescope.
James Webb was the NASA administrator during the 1960s Apollo program, but before that, he was undersecretary of the US State Department in the 1950s, and has been accused of acquiescing to and enforcing the then-US Government policy of LGBTQ persecution, which eventually culminated in the "Lavender Scare", one of the darkest episodes in recent US history.
There is archival evidence that Webb knew of this policy and that it was forcing LGBTQ civil servants out of the government, ending careers and destroying lives in the process. There is also evidence of his participation in US Senate discussions that ultimately led to anti-LGBTQ federal policy.
Much of this is disputed by others, who argue that Webb was no different than any other administrator at the time and had no control over setting US government policy, no matter how backward and vile it might be.
There is no evidence of Webb's direct involvement in anti-LGBTQ persecution or specific actions he took to purge LGBTQ civil servants from the government. Still, many have called for the James Webb Space Telescope to be renamed in light of what evidence does exist of his complicity in the anti-LGBTQ policies of the US government at the time.
It should also be noted that it is out of step with tradition to name a space telescope after a US government official. Traditionally, space telescopes and other astronomical instruments are named for noted astronomers and scientists who furthered our understanding of the universe, i.e., Edwin Hubble.
For what it's worth, I would have liked to see the James Webb Space Telescope renamed, if for no other reason than to ensure that it could be something we could all get behind and celebrate without anyone feeling left out, ignored, or worse. That is out of my hands though, as NASA's decision on the name after reviewing the evidence is final, and they are not changing it.
Hopefully, in time, James Webb might come to mean something different for people, but that is not for me to say, as these are not my experiences and I have no right to speak for others who are offended by our honoring James Webb in this way.
If the episode can teach us anything, however, I hope that it is that we need to treat each other with kindness, compassion, and generosity in the future.
When we look out into the vast, unfathomable expanse of the universe, I hope it inspires humility in us all; that it reminds us that we are, in Carl Sagan's immortal words, a "mote of dust" in the cosmos, and that our prejudices aren't laws of nature but choices we all choose to make.
We can choose differently, and I hope for all our sakes that we do just that so we can all move into the future, bound together by the bonds of our shared humanity, and united in awe at the spectacular vision of the universe around us.
Merry Christmas, y'all.
Most Popular


